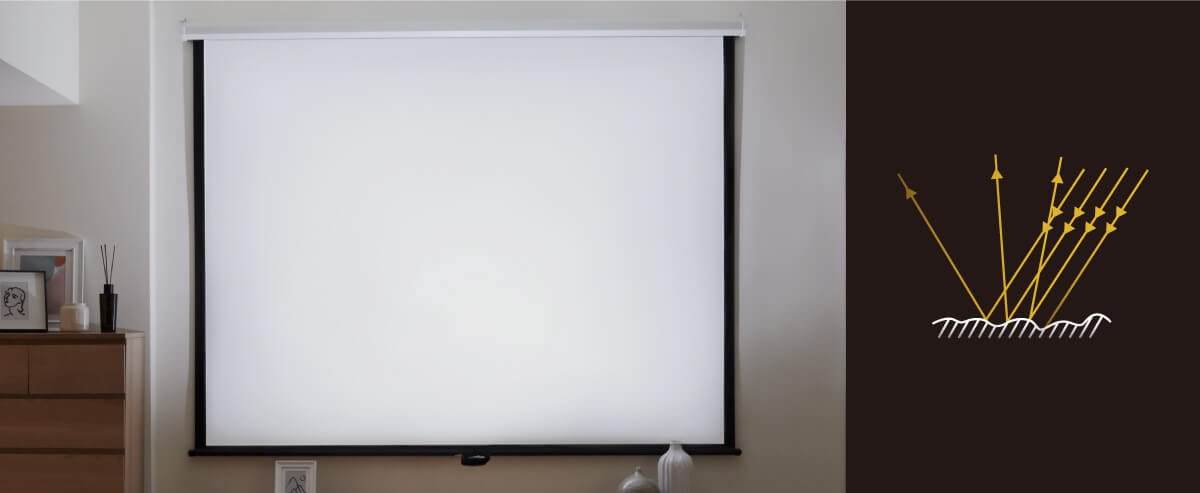
Projector
Explore All Projector Series
By Trending Word
4K UHD (3840×2160) Short Throw 2D, Vertical/Horizontal Keystone LED Laser With Android TV With Low Input LagExplore Commercial Projector
Professional Installation Exhibition & Simulation Small Business & Corporation K12 & Higher Education Golf Simulator ProjectorMonitor
Lighting
Explore All Lighting Series
By Series
Monitor Light BarInteractive Display
Remote Work & Learning
e-Store